Subaru and its AWD system
1. Purpose of All-Wheel Drive (AWD):
AWD systems provide power to all four wheels, improving traction and stability.
They offer drivers confidence during challenging weather conditions.
2. Subaru’s Innovations:
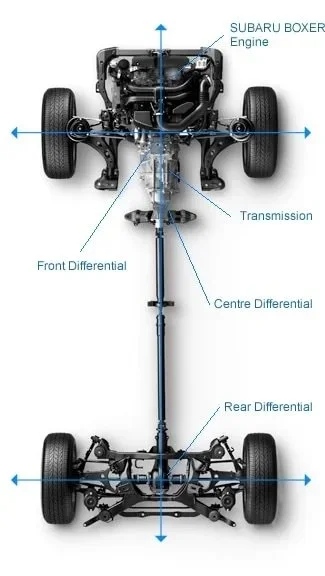
Subaru is a leading manufacturer of AWD vehicles, with their exclusive Symmetrical All-Wheel Drive (SAWD) system enhancing safety and reliability on various terrains.
SAWD includes a horizontally opposed Boxer engine that helps distribute weight and power evenly, ensuring optimal vehicle performance.
3. Mechanics of AWD:
AWD allows simultaneous power delivery to both front and rear wheels, compensating when one wheel lacks grip.
There are two main types of AWD systems:
Full-time AWD: Power is always sent to all four wheels, ensuring constant traction.
Part-time AWD: Only two wheels receive power until additional traction is required.
4. Benefits of Full-time AWD:
It provides quicker responses to wheel slippage, enhancing control and safety.
5. Driving Safety:
Subaru emphasizes the importance of caution in driving, even with advanced AWD technology, as no vehicle is completely invincible.
6. Connection Between SAWD and Driving Experience:
The symmetrical design and low center of gravity of Subaru's Boxer engine contribute to stability and responsiveness.
This combination allows for better control in challenging driving situations, enhancing passenger comfort and safety.
On the Newer models that are available today they also have more Enhanced features for difficult terrain
On many Subaru models, the AWD system works in tandem with specialized software for increased capability:
X-MODE: This system is available on certain models and offers enhanced settings for difficult terrain like snow, dirt, and mud. It works with the AWD system by adjusting engine output, transmission, and braking to provide even more traction and control.
Dual-Function X-MODE: Found on Wilderness models, this system provides additional traction settings for deep snow, mud, and sand.
Variable Torque Distribution (VTD): Designed for performance-oriented models with automatic transmissions, VTD systems have a rear-biased torque split under normal driving (e.g., 45% front, 55% rear). This provides sportier handling characteristics and can shift power up to 50/50 when needed.
hope this covers the main advantages of subarus AWD systems
next lets explore the DCCD even more.
Subaru and its AWD system